树
1.二叉树的前序遍历
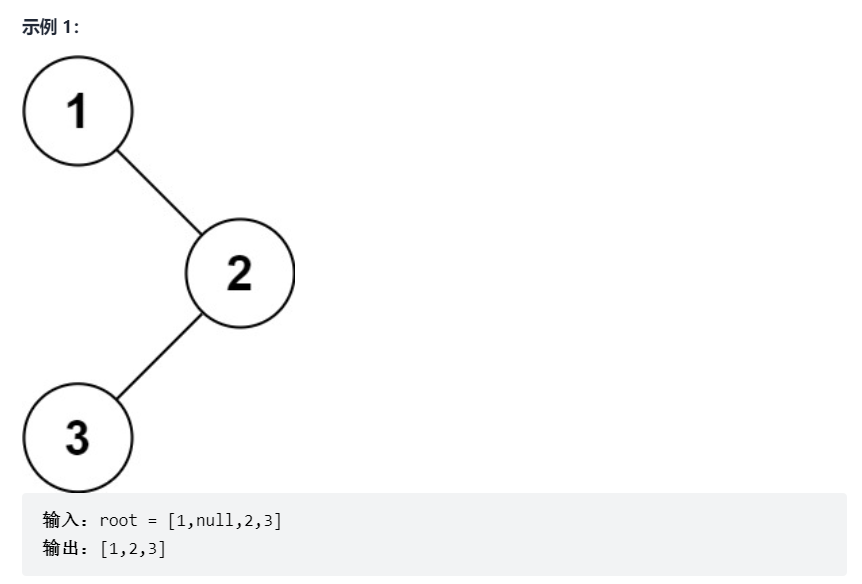
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历。
思路:递归和迭代,前序遍历为中-左-右
递归
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
if (!root) return []
const res = []
preorder(root, res)
return res
}
var preorder = function(node, res) {
if (!node) return
res.push(node.val)
preorder(node.left, res)
preorder(node.right, res)
}迭代
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
if (!root) return []
const stack = [], res = []
stack.push(root)
while (stack.length) {
const curr = stack.pop()
res.push(curr.val)
if (curr.right) stack.push(curr.right)
if (curr.left) stack.push(curr.left)
}
return res
};
2.二叉树的中序遍历
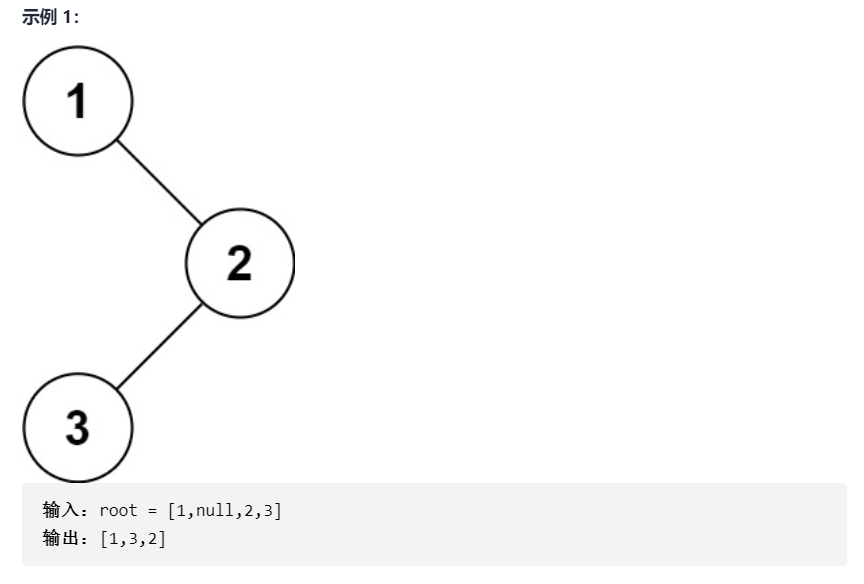
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
思路:
迭代和递归,中序的顺序:左-中-右
迭代
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
const res = [];
const stk = [];
while (root || stk.length) {
while (root) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
res.push(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
};递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
const res = []
const inorder = (root) =>{
if(!root){
return
}
inorder(root.left)
res.push(root.val)
inorder(root.right)
}
inorder(root)
return res
};3.二叉树的后序遍历
给定一个二叉树,返回它的 后序 遍历。
思路:迭代和递归
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
let result = [];
this.postOrder = function(root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
// 后序遍历位置
result.push(root.val);
}
postOrder(root);
return result;
};4.二叉树的层序遍历
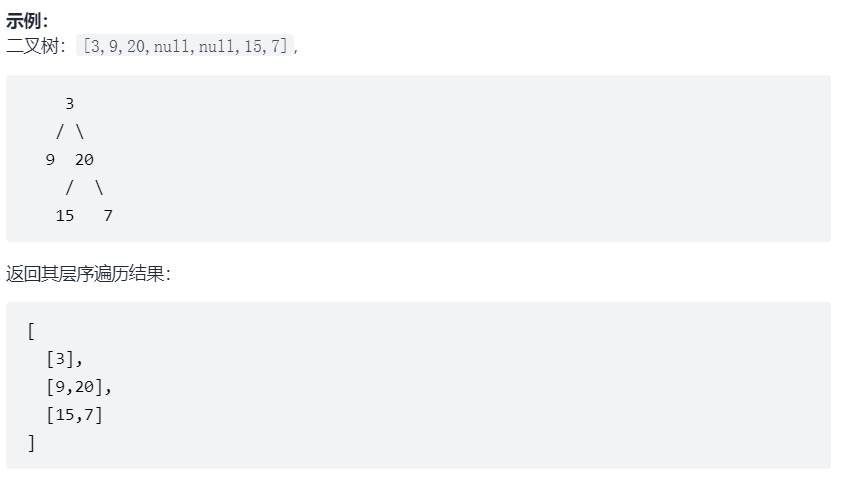
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。(即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
var levelOrder = function(root) {
//二叉树的层序遍历
let res=[],queue=[];
queue.push(root);
if(root===null){
return res;
}
while(queue.length!==0){
// 记录当前层级节点数
let length=queue.length;
//存放每一层的节点
let curLevel=[];
for(let i=0;i<length;i++){
let node=queue.shift();
curLevel.push(node.val);
// 存放当前层下一层的节点
node.left&&queue.push(node.left);
node.right&&queue.push(node.right);
}
//把每一层的结果放到结果数组
res.push(curLevel);
}
return res;
};5.二叉树的最大深度
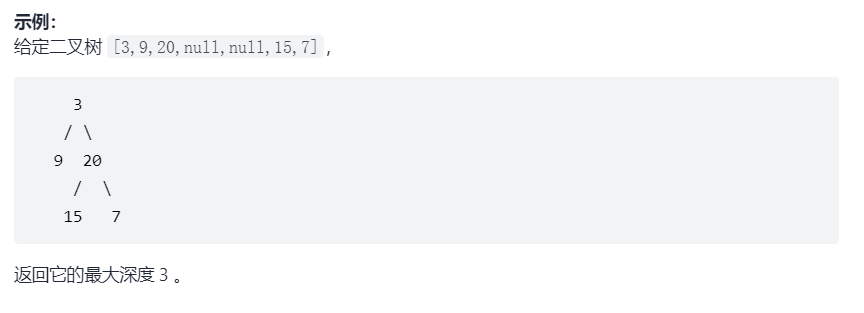
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) {
return 0;
} else {
const left = maxDepth(root.left);
const right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
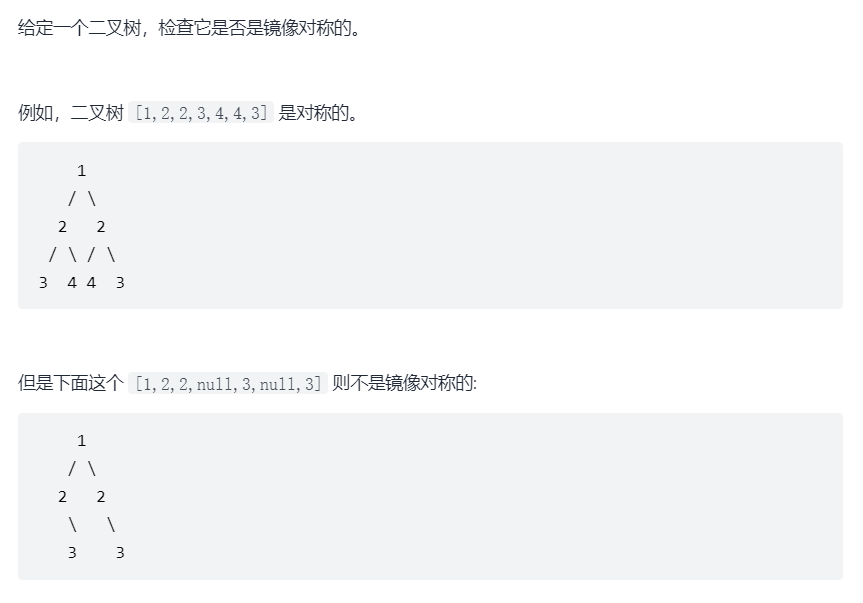
};6.对称二叉树
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
//使用递归遍历左右子树 递归三部曲
// 1. 确定递归的参数 root.left root.right和返回值true false
const compareNode=function(left,right){
//2. 确定终止条件 空的情况
if(left===null&&right!==null||left!==null&&right===null){
return false;
}else if(left===null&&right===null){
return true;
}else if(left.val!==right.val){
return false;
}
//3. 确定单层递归逻辑
let outSide=compareNode(left.left,right.right);
let inSide=compareNode(left.right,right.left);
return outSide&&inSide;
}
if(root===null){
return true;
}
return compareNode(root.left,root.right);
};7.翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。
var invertTree = function(root) {
if (root === null) {
return null;
}
const left = invertTree(root.left);
const right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
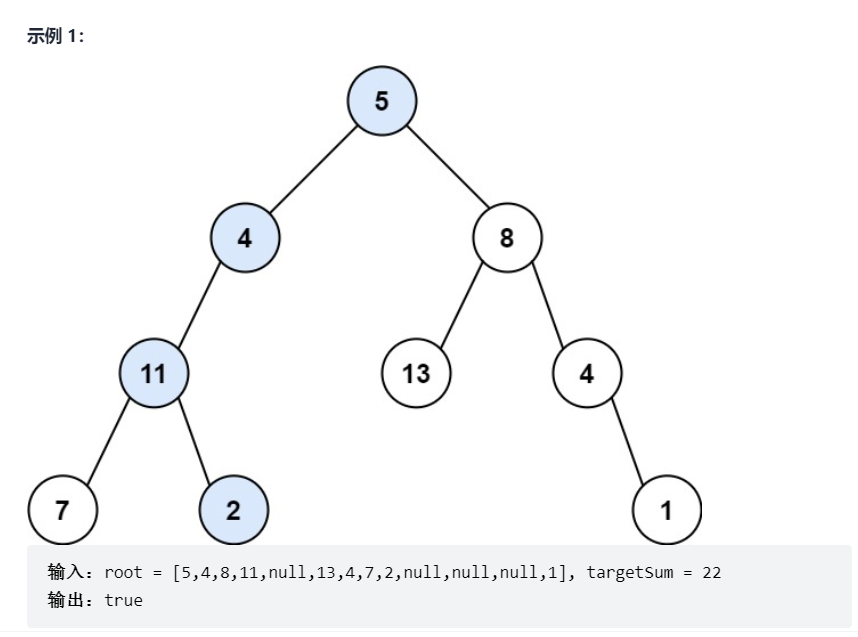
};8.路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum ,判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
var hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
// 节点不存在 返回false
if(!root) return false
// 左右子树都不存在,说明是叶子节点,判断是否符合条件
if(!root.left && !root.right) return targetSum === root.val
// 到这里就是:节点存在,左右子树存在一个或者都存在,也就是内部节点
// 遍历左右子树,更新总和为 总和删除当前节点的值
return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val)
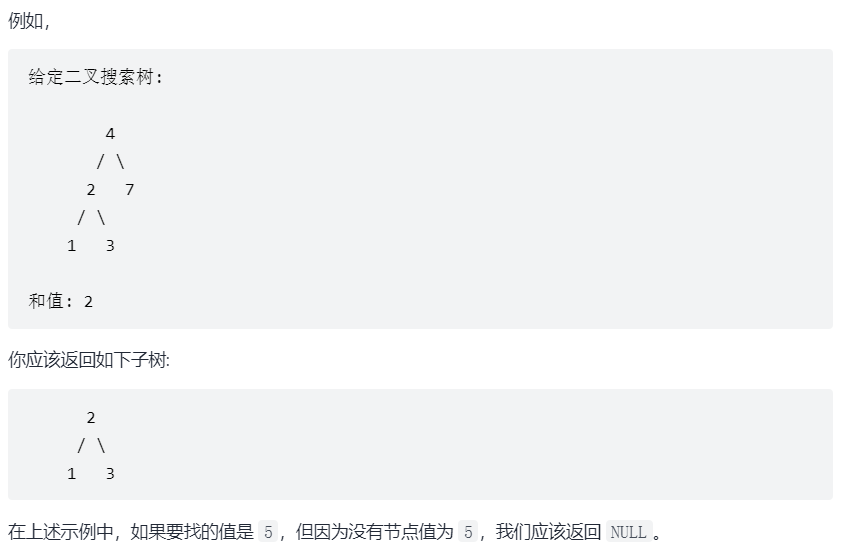
};9.二叉搜索树中的搜索
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和一个值。 你需要在BST中找到节点值等于给定值的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 NULL。
例如,
思路:
递归和迭代
递归:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} val
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var searchBST = function (root, val) {
if (!root || root.val === val) {
return root;
}
if (root.val > val)
return searchBST(root.left, val);
if (root.val < val)
return searchBST(root.right, val);
return null;
};
迭代:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} val
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var searchBST = function (root, val) {
while (root !== null) {
if (root.val > val)
root = root.left;
else if (root.val < val)
root = root.right;
else
return root;
}
return root;
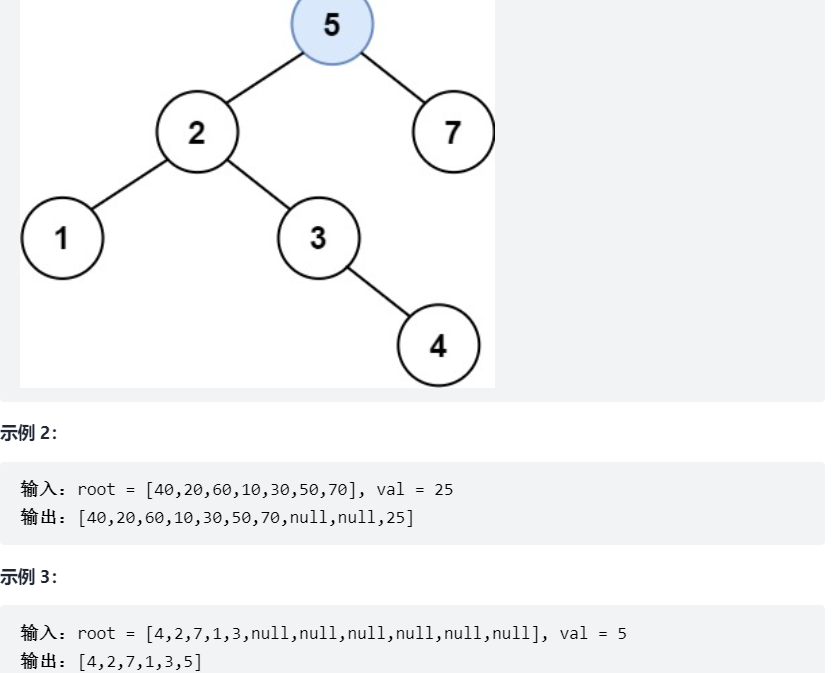
};10.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和要插入树中的值,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。
注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回**任意有效的结果 **。
思路:
因此,当将val 插入到以root 为根的子树上时,根据 val 与root.val 的大小关系,就可以确定要将 val 插入到哪个子树中。
如果该子树不为空,则问题转化成了将val 插入到对应子树上。
否则,在此处新建一个以val 为值的节点,并链接到其父节点root 上。
var insertIntoBST = function(root, val) {
if (root === null) {
return new TreeNode(val);
}
let pos = root;
while (pos !== null) {
if (val < pos.val) {
if (pos.left === null) {
pos.left = new TreeNode(val);
break;
} else {
pos = pos.left;
}
} else {
if (pos.right === null) {
pos.right = new TreeNode(val);
break;
} else {
pos = pos.right;
}
}
}
return root;
};
11.验证二叉搜索树
给你一个二叉树的根节点root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
节点的左子树只包含小于 当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
思路:
要解决这道题首先我们要了解二叉搜索树有什么性质可以给我们利用,由题目给出的信息我们可以知道:如果该二叉树的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;它的左右子树也为二叉搜索树。
const helper = (root, lower, upper) => {
if (root === null) {
return true;
}
if (root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper) {
return false;
}
return helper(root.left, lower, root.val) && helper(root.right, root.val, upper);
}
var isValidBST = function(root) {
return helper(root, -Infinity, Infinity);
};12.两数之和IV-输入BST
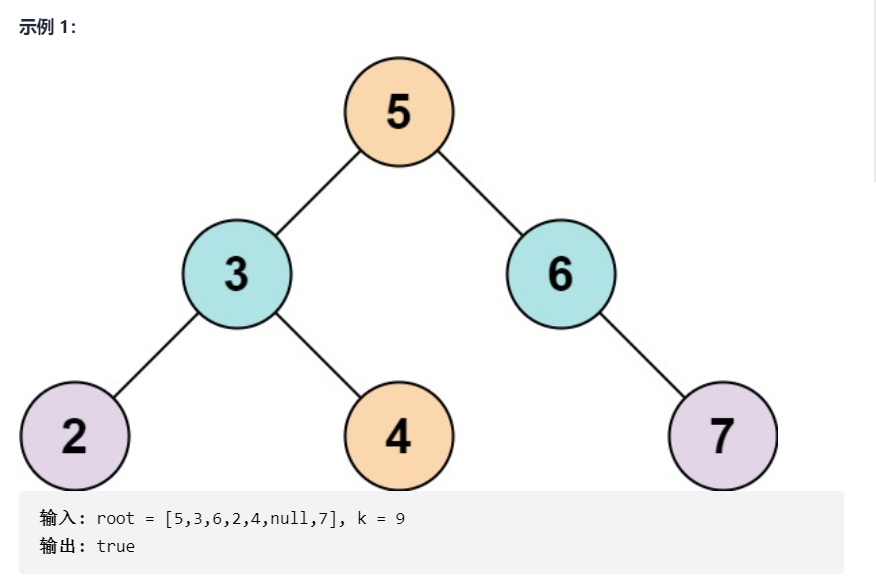
给定一个二叉搜索树 root 和一个目标结果 k,如果 BST 中存在两个元素且它们的和等于给定的目标结果,则返回 true。
思路:
哈希表,迭代法,前序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} k
* @return {boolean}
*/
var findTarget = function(root, k) {
let myMap = new Map()
let queue = []
if(!root){
return false
}
queue.push(root)
while(queue.length){
let i=0
let curNode = queue.pop()
deffer = k - curNode.val
if(myMap.has(deffer)){
return true
}
myMap.set(curNode.val,i)
if(curNode.left !=null){
queue.push(curNode.left)
}
if(curNode.right !=null){
queue.push(curNode.right)
}
i++
}
return false
};13.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
// 使用递归的方法
// 1. 使用给定的递归函数lowestCommonAncestor
// 2. 确定递归终止条件
if(root === null) {
return root;
}
if(root.val>p.val&&root.val>q.val) {
// 向左子树查询
let left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
return left !== null&&left;
}
if(root.val<p.val&&root.val<q.val) {
// 向右子树查询
let right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
return right !== null&&right;
}
return root;
};